[CyberLand News] Weekly #22 - Threats and Malware
Last news on threats, malware and vulnerabilties in the cyber land
Contents
Ongoing Exploitation Attempts Target Apache RocketMQ Vulnerabilities
Russian Hackers Sandworm Wipe Kyivstar's Network in Destructive Cyberattack
Google's Mandiant Faces Security Breach Leading to Cryptocurrency Scam on Twitter
Critical Flaws in Google Kubernetes Engine Expose Vulnerabilities Leading to Potential Cluster Takeover
Advanced DLL Hijacking Technique Exploits Trusted WinSxS Executables on Windows 10 and 11
Ongoing Exploitation Attempts Target Apache RocketMQ Vulnerabilities
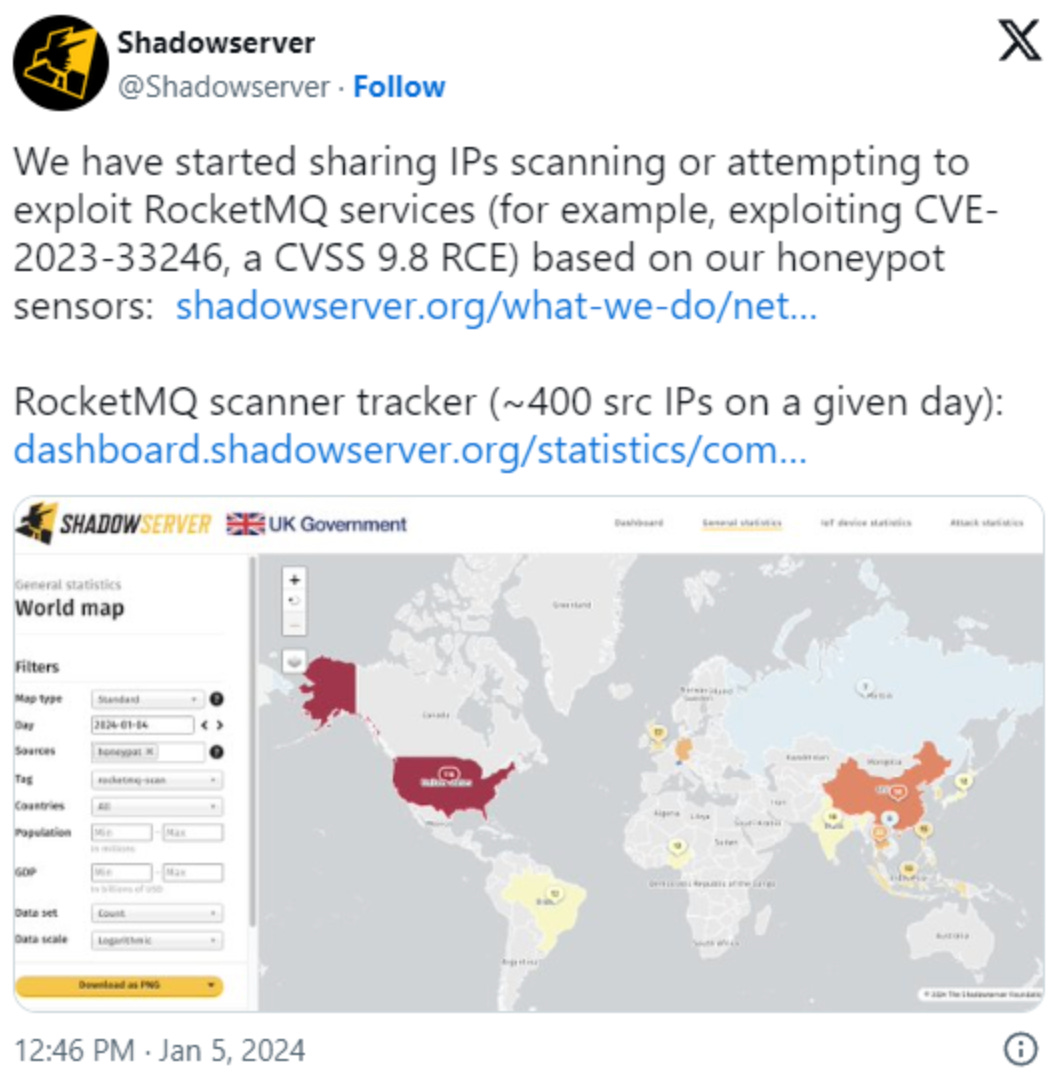
Security researchers have identified ongoing attempts to exploit vulnerabilities (CVE-2023-33246 and CVE-2023-37582) in Apache RocketMQ services, known for a remote command execution flaw. The vulnerabilities were initially addressed in a May 2023 patch, but the fix was incomplete for the NameServer component in RocketMQ versions 5.1 and older. The remaining flaw (CVE-2023-37582) allows attackers to execute commands when the NameServer address is exposed online without proper permission checks. Exploitation involves using the update configuration function. The researcher advises upgrading NameServer to version 5.1.2/4.9.7 or above to mitigate the risk of attacks. Threat intelligence from The ShadowServer Foundation indicates numerous hosts scanning for exposed RocketMQ systems.
More details in “CVE-2023-37582 Detail“
Additional info in “Apache RocketMQ: Possible remote code execution when using the update configuration function“
Additional info in “ShadowServer stats“
Russian Hackers Sandworm Wipe Kyivstar's Network in Destructive Cyberattack
Russian Sandworm Hackers Wipe Kyivstar's Network: A cyberattack orchestrated by the Russian military hacking group Sandworm, also known as Solntsepek, has led to the complete wiping of Ukraine's largest telecommunications service provider, Kyivstar. The breach, which occurred in May 2023, resulted in a destructive attack in December that wiped thousands of virtual servers and computers, crippling Kyivstar's core network. The impact affected the country's civilian population, but military communications remained largely unaffected due to Ukraine's Defense Forces employing different communication protocols. The Solntsepek group claimed responsibility for the attack, stating that they targeted Kyivstar for providing communications to the Armed Forces of Ukraine. This incident follows previous breaches by Sandworm, as reported in an October 2023 CERT-UA report, which revealed the hacking group's involvement in breaching the networks of 11 Ukrainian telecom service providers since May 2023.
Additional info in “Exclusive: Russian hackers were inside Ukraine telecoms giant for months“
Additional info in link
Google's Mandiant Faces Security Breach Leading to Cryptocurrency Scam on Twitter
On January 3, 2024, at around 8:00 PM, Google's cybersecurity firm Mandiant (formerly known as Twitter) faced a security breach in its X account. The breach was exploited by unidentified hackers, crypto scammers, who targeted the firm's extensive follower base of over 122,000 users.
The hackers executed a cryptocurrency scam using Mandiant's compromised account, tweeting links to the Phantom cryptocurrency wallet. Posing as Phantom, they promoted a fake airdrop to lure users. The attackers even changed Mandiant's Twitter handle to "@phantomsolw."
Although Mandiant eventually regained control of the account, restoring it to its original state proved challenging due to Twitter's restrictions on frequent name changes. However, as of the latest update, Mandiant's Twitter account has been successfully restored, and the malicious links have been removed.
This incident follows a pattern of high-profile Twitter account hacks for cryptocurrency scams. Notably, in July 2020, several prominent figures and companies, including Barack Obama, Joe Biden, Bill Gates, Elon Musk, and others, fell victim to similar attacks. The hacking of a cybersecurity company like Mandiant raises concerns, emphasizing the ongoing challenges in addressing phishing and disinformation on the platform, particularly with scammers selling verified Twitter accounts, exacerbating the issue.
Critical Flaws in Google Kubernetes Engine Expose Vulnerabilities Leading to Potential Cluster Takeover
Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) has been identified with two vulnerabilities that could be exploited by threat actors with existing access to the Kubernetes cluster, potentially resulting in severe damage. The first flaw is associated with FluentBit, GKE's default logging agent, while the second pertains to Anthos Service Mesh (ASM) and its default privileges. If an attacker gains sufficient privileges within a FluentBit container with ASM installed, a chain of attacks could lead to full control over the Kubernetes cluster. This could enable data theft, deployment of malicious pods, and disruption of cluster operations. Google addressed the configuration issue in mid-December 2023, but the discovery highlights the importance of ongoing vigilance in securing Kubernetes environments.
More details in “Dual Privilege Escalation Chain: Exploiting Monitoring and Service Mesh Configurations and Privileges in GKE to Gain Unauthorized Access in Kubernetes“
Additional info in “Multiple Flaws In Google Kubernetes Engine Let Attackers Escalate Privileges“
Advanced DLL Hijacking Technique Exploits Trusted WinSxS Executables on Windows 10 and 11
Security researchers at Security Joes have uncovered a sophisticated DLL hijacking technique that leverages trusted WinSxS executables, allowing threat actors to bypass Windows mechanisms. DLL hijacking involves placing a malicious DLL in a directory searched by a vulnerable application before the legitimate one, enabling the execution of arbitrary code and compromising the system. The new technique exploits DLL Search Order Hijacking, targeting trusted WinSxS executables. By manipulating apps with predefined search orders, threat actors can execute malicious code within Windows folders without requiring additional binaries. This technique is compatible with both Windows 10 and 11 and evades high privilege requirements, enhancing stealth in compromising systems and evading detection. The WinSxS folder, critical for version management, system integrity, and dynamic activation in Windows OS, becomes a potential target for these sophisticated attacks.
More details in “Hide and Seek in Windows' Closet: Unmasking the WinSxS Hijacking Hideout“
Additional info in “PoC Video”
A.I. support for text drafting